 04-技术讲解
04-技术讲解
# 实时协作技术讲解
# 什么问题
- 在线的文档编辑器
- 在线白板功能
- 在线的电子表格
- ....
实时协作开发会遇到的问题:
- 实时通信
- 编辑冲突以及文档的一致性
- 离线编辑和数据同步
# 解决思路
- 实时通信:WebSocket 提供一个持久的双向通信通道
- 编辑冲突与一致性:这个涉及到一些算法
- OT
- CRDT
- 离线编辑和数据同步:使用 IndexedDB 来本地存储编辑操作的日志,联网之后就需要同步离线时所编辑的内容。
# 技术细节
# 1. 整体流程
整体架构如下:
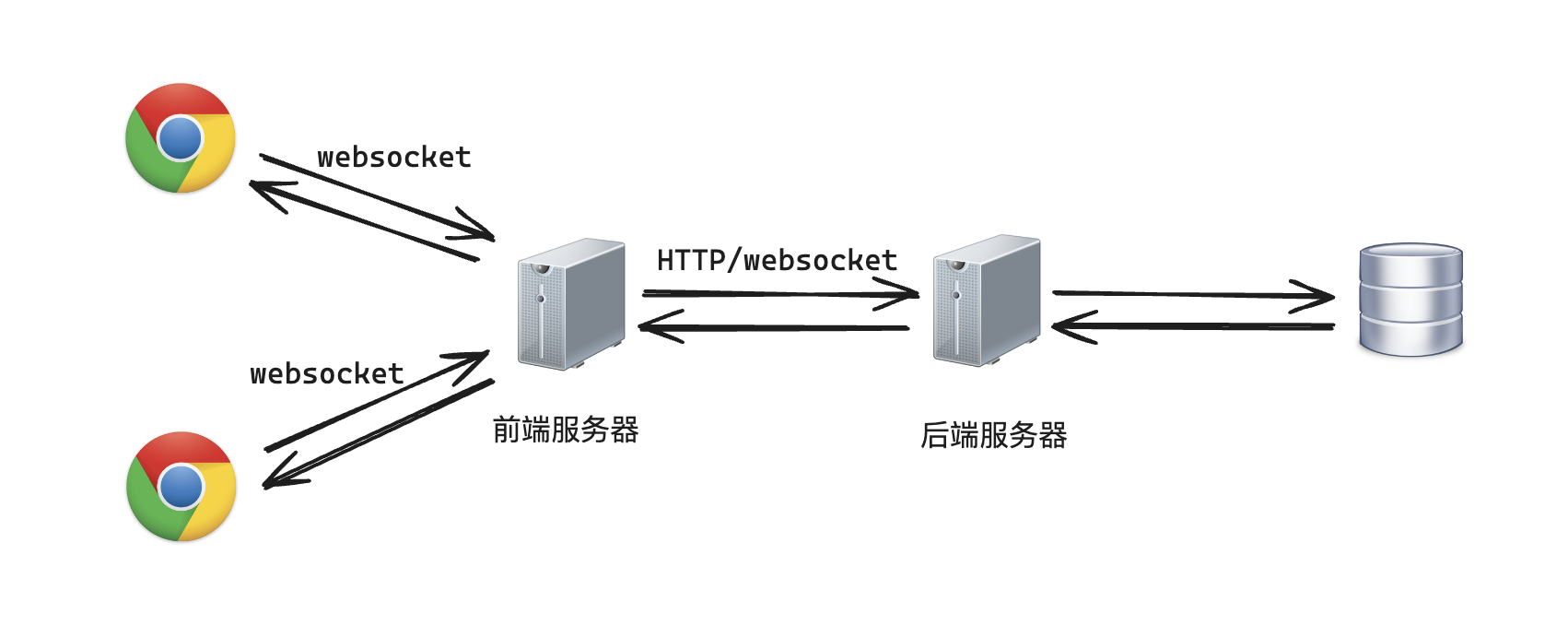
- 客户端与前端服务器的交互
- 建立连接:客户 A 和客户 B 都与前端服务器建立 WebSocket 连接。
- 发送操作:当客户 A 进行编辑操作时,操作通过 WebSocket 连接发送到前端服务器。同样,客户 B 的操作也通过其 WebSocket 连接发送到前端服务器。
- 前端服务器的职责
- 接收操作:前端服务器接收到来自客户 A 和客户 B 的编辑操作。
- 初步处理:前端服务器可以对这些操作进行初步处理,比如进行简单的验证、过滤,或是进行某些预处理(如记录日志、缓存等)。
- 转发操作:前端服务器将处理后的编辑操作转发给后端服务器。
- 后端服务器的职责
- 接收操作:后端服务器接收到来自前端服务器的编辑操作。
- 冲突解决:后端服务器使用 OT 或 CRDT 算法来处理冲突,并合并操作,确保文档的一致性。
- 数据持久化:将合并后的编辑操作实时存储到数据库中,并更新文档的最新状态。
- 同步更新:后端服务器将最新的文档状态发送回前端服务器。
- 前端服务器的回传:前端服务器接收到后端服务器传回的最新文档状态后,通过 WebSocket 将最新状态广播给所有连接的客户端
具体流程实例
客户A编辑操作:
客户A输入 "Hello" -> 通过WebSocket发送到前端服务器。
前端服务器接收 "Hello" -> 转发给后端服务器。
后端服务器接收 "Hello" -> 进行冲突解决和合并 -> 存储到数据库。
后端服务器返回最新状态 "Hello" -> 前端服务器接收并广播。
客户B接收更新:客户B通过WebSocket接收前端服务器广播的最新状态 "Hello"。
客户B编辑操作:
客户B输入 " World" -> 通过WebSocket发送到前端服务器。
前端服务器接收 " World" -> 转发给后端服务器。
后端服务器接收 " World" -> 进行冲突解决和合并(与 "Hello" 合并为 "Hello World") -> 存储到数据库。
后端服务器返回最新状态 "Hello World" -> 前端服务器接收并广播。
客户A接收更新:客户A通过WebSocket接收前端服务器广播的最新状态 "Hello World"。
# 2. 前端通信
整个通信分为:前端通信 和 后端通信
前端通信主要是指 客户端 和 前端服务器 之间的通信,这里建立的是 Webscoket 连接,这里在通信的时候还可以传递一个操作类型(type)值,主要是用于后端通信的时候使用。
示例代码如下:
class CollaborationClient {
constructor() {
this.ws = new WebSocket('wss://frontend-server/ws');
this.ws.onopen = this.handleWebSocketOpen.bind(this);
this.ws.onclose = this.handleWebSocketClose.bind(this);
this.ws.onmessage = this.handleWebSocketMessage.bind(this);
this.pendingOperations = [];
}
// WebSocket打开时处理
handleWebSocketOpen() {
console.log('WebSocket connection opened.');
// 发送所有待处理的操作
this.pendingOperations.forEach(operation => this.ws.send(JSON.stringify(operation)));
this.pendingOperations = [];
}
// WebSocket关闭时处理
handleWebSocketClose() {
console.log('WebSocket connection closed.');
}
// WebSocket消息处理
handleWebSocketMessage(event) {
const message = JSON.parse(event.data);
console.log('WebSocket message received:', message);
}
// 发送操作
sendOperation(operation) {
if (this.ws.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN) {
this.ws.send(JSON.stringify(operation));
} else {
this.pendingOperations.push(operation);
}
}
}
// 使用示例
const client = new CollaborationClient();
// 发送普通操作(通过WebSocket传输给前端服务器)
client.sendOperation({ type: 'normal', content: 'Save draft content' });
// 发送实时操作(通过WebSocket传输给前端服务器)
client.sendOperation({ type: 'realtime', content: 'User is typing...' });
# 3. 后端通信
指的是 前端服务器 和 后端服务器 之间的通信。这里通信采用的是混合方法:
- HTTP:保存草稿、后台同步...
- Webscoket:实时编辑、共同绘图...
这个时候就根据 type 值来决定建立什么样的连接。
前端服务器示例代码:
const WebSocket = require('ws');
const http = require('http');
const fetch = require('node-fetch');
// 建立与后端服务器的WebSocket连接
const backendWs = new WebSocket('ws://backend-server/ws');
backendWs.on('open', () => {
console.log('Connected to backend WebSocket server');
});
backendWs.on('message', (message) => {
console.log('Message from backend WebSocket server:', message);
});
const wss = new WebSocket.Server({ noServer: true });
wss.on('connection', (ws) => {
ws.on('message', (message) => {
const operation = JSON.parse(message);
if (operation.type === 'realtime') {
// 实时操作通过WebSocket转发给后端服务器
backendWs.send(JSON.stringify(operation));
} else {
// 普通操作通过HTTP转发给后端服务器
forwardToBackendViaHttp(operation);
}
});
});
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
res.writeHead(404);
res.end();
});
server.on('upgrade', (request, socket, head) => {
wss.handleUpgrade(request, socket, head, (ws) => {
wss.emit('connection', ws, request);
});
});
server.listen(8080);
function forwardToBackendViaHttp(operation) {
fetch('http://backend-server/api/normal-operation', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify(operation)
}).then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
console.log('Response from backend HTTP server:', data);
});
}
后端服务器(以 Node.js 为例)
const WebSocket = require('ws');
const http = require('http');
const wss = new WebSocket.Server({ noServer: true });
wss.on('connection', (ws) => {
ws.on('message', (message) => {
const operation = JSON.parse(message);
handleRealTimeOperation(operation);
});
});
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
if (req.method === 'POST' && req.url === '/api/normal-operation') {
let body = '';
req.on('data', chunk => {
body += chunk.toString();
});
req.on('end', () => {
const operation = JSON.parse(body);
handleNormalOperation(operation);
res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' });
res.end(JSON.stringify({ status: 'success' }));
});
} else {
res.writeHead(404, { 'Content-Type': 'text/plain' });
res.end('Not Found');
}
});
server.on('upgrade', (request, socket, head) => {
wss.handleUpgrade(request, socket, head, (ws) => {
wss.emit('connection', ws, request);
});
});
server.listen(8081, () => {
console.log('Backend server listening on port 8081');
});
function handleRealTimeOperation(operation) {
// 实时操作处理逻辑
console.log('Real-time operation:', operation);
// 此处可以添加对实时操作的具体处理逻辑,例如更新文档内容、通知其他客户端等
}
function handleNormalOperation(operation) {
// 普通操作处理逻辑
console.log('Normal operation:', operation);
// 此处可以添加对普通操作的具体处理逻辑,例如保存草稿、加载历史记录等
}
最后整理一下流程:
初始连接:
客户端与前端服务器建立 WebSocket 连接用于实时操作。
同时前端服务器使用 HTTP 连接后端服务器,用于一些初始化数据加载和非实时操作。
普通操作:
非实时操作,如保存草稿、加载历史记录等,仍然是通过 HTTP 请求处理。
前端服务器通过 HTTP 将这些请求转发给后端服务器。
后端服务器处理请求并返回结果。
实时操作:
实时操作,如编辑操作、实时协作,则切换为 WebSocket 连接来处理。
前端服务器通过 WebSocket 将这些操作实时转发给后端服务器。
后端服务器处理操作并通过 WebSocket 返回结果。
切换机制:
- 前端服务器根据具体的业务逻辑和操作类型(由操作类型 type 决定)选择合适的通信协议。
- 当然,在系统中还可以加入自动检测机制(这是一个优化的方向,这个优化的方向实现后,就不需要 type 值了):
- 当系统检测到需要实时性的关键操作时,前端服务器使用 WebSocket 连接与后端服务器通信。
- 当系统检测到处于低实时性需求状态时,前端服务器使用 HTTP 请求与后端服务器通信。
# 4. 安全验证
整个架构因为涉及到了 BFF 层,所以安全验证的工作也是咱们前端来做的。
- 用户名和密码
- OAuth
- JWT
- SSO
这里以 JWT 为例。
客户端代码示例:
class CollaborationClient {
constructor() {
this.ws = null;
this.pendingOperations = [];
this.token = null; // 存储JWT令牌
}
// 用户登录并获取JWT令牌
async login(username, password) {
const response = await fetch('https://frontend-server/login', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({ username, password })
});
const data = await response.json();
if (data.token) {
this.token = data.token;
// 验证通过之后,建立 Webscoket 连接
this.connectWebSocket();
} else {
console.error('Login failed');
}
}
// 连接WebSocket
connectWebSocket() {
this.ws = new WebSocket('wss://frontend-server/ws');
this.ws.onopen = this.handleWebSocketOpen.bind(this);
this.ws.onclose = this.handleWebSocketClose.bind(this);
this.ws.onmessage = this.handleWebSocketMessage.bind(this);
}
// WebSocket打开时处理
handleWebSocketOpen() {
console.log('WebSocket connection opened.');
// 发送身份验证令牌
this.ws.send(JSON.stringify({ type: 'auth', token: this.token }));
// 发送所有待处理的操作
this.pendingOperations.forEach(operation => this.ws.send(JSON.stringify(operation)));
this.pendingOperations = [];
}
// WebSocket关闭时处理
handleWebSocketClose() {
console.log('WebSocket connection closed.');
}
// WebSocket消息处理
handleWebSocketMessage(event) {
const message = JSON.parse(event.data);
console.log('WebSocket message received:', message);
}
// 发送操作
sendOperation(operation) {
if (this.ws && this.ws.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN) {
this.ws.send(JSON.stringify(operation));
} else {
this.pendingOperations.push(operation);
}
}
}
// 使用示例
const client = new CollaborationClient();
// 用户登录并获取JWT令牌
client.login('username', 'password').then(() => {
// 发送普通操作(通过WebSocket传输给前端服务器)
client.sendOperation({ type: 'normal', content: 'Save draft content' });
// 发送实时操作(通过WebSocket传输给前端服务器)
client.sendOperation({ type: 'realtime', content: 'User is typing...' });
});
前端服务器端,也需要增加针对 JWT 这一块儿的处理:
const WebSocket = require('ws');
const http = require('http');
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
// 创建一个WebSocket服务器
const wss = new WebSocket.Server({ noServer: true });
// WebSocket连接处理
wss.on('connection', (ws) => {
ws.on('message', (message) => {
const operation = JSON.parse(message);
// 身份验证
if (operation.type === 'auth') {
jwt.verify(operation.token, 'your-secret-key', (err, user) => {
if (err) {
ws.send(JSON.stringify({ type: 'error', message: 'Authentication failed' }));
ws.close();
} else {
ws.user = user;
ws.send(JSON.stringify({ type: 'success', message: 'Authentication successful' }));
}
});
} else if (ws.user) {
// 处理经过验证的操作
handleOperation(ws.user, operation);
} else {
ws.send(JSON.stringify({ type: 'error', message: 'Not authenticated' }));
}
});
});
// 处理经过验证的操作
function handleOperation(user, operation) {
// 实现具体的操作处理逻辑
console.log(`User ${user.username} performed operation:`, operation);
}
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
res.writeHead(404);
res.end();
});
server.on('upgrade', (request, socket, head) => {
wss.handleUpgrade(request, socket, head, (ws) => {
wss.emit('connection', ws, request);
});
});
server.listen(8080, () => {
console.log('Frontend server listening on port 8080');
});
# 5. 编辑冲突和一致性
- OT:核心思想是将操作进行转换
- CRDT:设定一种特定的数据类型来解决
1. OT
Operational Transformation:操作转换。最早应用于 Google Docs
基本概念:当两个操作冲突时,通过转换一个操作使其适应另一个操作。
优点:
- 已经被广泛应用和验证。
- 能够处理复杂的编辑场景,适用于需要实时协作和频繁编辑的场景。
缺点:实现较为复杂,需要额外的转换逻辑。
需求:假设有两个客户端同时在文档的位置 5 插入不同的字符,这里就涉及到编辑的冲突了
客户端A
{
"type": "insert",
"position": 5,
"content": "A"
}
客户端B
{
"type": "insert",
"position": 5,
"content": "B"
}
OT 转换:
class TextOperation {
constructor(type, position, content) {
this.type = type; // 操作类型: 'insert' 或 'delete'
this.position = position; // 操作的位置
this.content = content; // 插入或删除的内容
}
// 转换操作使其适应另一个操作
transformAgainst(other) {
// 如果另一个操作是插入操作
if (other.type === 'insert') {
if (this.type === 'insert') {
// 两个都是插入操作
if (this.position > other.position || (this.position === other.position && this.content > other.content)) {
// 如果当前操作的位置大于另一个操作的位置,或位置相同但内容在字母表中更大,则将当前操作的位置后移
this.position++;
}
} else if (this.type === 'delete') {
// 当前操作是删除,另一个操作是插入
if (this.position >= other.position) {
// 如果当前操作的位置大于等于另一个操作的位置,则将当前操作的位置后移
this.position++;
}
}
} else if (other.type === 'delete') {
if (this.type === 'insert') {
// 当前操作是插入,另一个操作是删除
if (this.position > other.position) {
// 如果当前操作的位置大于另一个操作的位置,则将当前操作的位置前移
this.position--;
}
} else if (this.type === 'delete') {
// 两个都是删除操作
if (this.position > other.position) {
// 如果当前操作的位置大于另一个操作的位置,则将当前操作的位置前移
this.position--;
} else if (this.position === other.position) {
// 如果两个操作的位置相同,则两个删除操作相互抵消
return null; // 返回null表示操作被抵消
}
}
}
return this; // 返回转换后的操作
}
}
// 创建两个操作,模拟两个客户端的操作
const operationA = new TextOperation('insert', 5, 'A');
const operationB = new TextOperation('insert', 5, 'B');
// 将操作A转换为适应操作B
const transformedA = operationA.transformAgainst(operationB);
// 将操作B转换为适应操作A
const transformedB = operationB.transformAgainst(transformedA);
console.log(transformedA); // TextOperation { type: 'insert', position: 6, content: 'A' }
console.log(transformedB); // TextOperation { type: 'insert', position: 5, content: 'B' }
OT 算法是双向的,这里操作A和操作B冲突了,那么会针对两个操作都进行转换。
在转换操作B的时候,会基于转换后的操作A再来做转换。
2. CRDT 算法
这种算法的全称:Conflict-free Replicated Data Types,核心思想是设计一个特殊的数据类型,操作用这个特殊的数据类型来存储,内部可以针对这个特殊数据类型进行很方便排序操作。
基本概念:
- 可交换操作:操作之间不需要转换,顺序不会影响结果。
- 数据类型:设计特定的数据结构,如 G-Counter, PNCounter, RGA 等。
优点:
- 操作顺序不影响最终结果,简化了处理逻辑。
- 更适合分布式系统。
缺点:
- 需要设计特定的数据类型,不适用于所有场景。
- 在某些复杂的应用场景下实现较为复杂。
定义一个 CRDT 类:
class CRDT {
constructor() {
this.data = []; // 用于存储字符的数组
}
// 插入操作
insert(id, pos, char) {
// 插入字符到指定位置,并附带唯一的ID
this.data.splice(pos, 0, { id, char });
// 按位置和ID排序,确保顺序一致
this.data.sort(
(a, b) => a.position - b.position || a.id.localeCompare(b.id)
);
}
// 删除操作
delete(id, pos) {
// 删除时根据位置和ID找到并删除
this.data = this.data.filter(
(item, index) => index !== pos || item.id !== id
);
}
// 应用操作
apply(operation) {
if (operation.type === "insert") {
this.insert(operation.id, operation.position, operation.content);
} else if (operation.type === "delete") {
this.delete(operation.id, operation.position);
}
}
// 获取数据
getData() {
return this.data.map((item) => item.char).join("");
}
}
模拟操作:假设有两个客户端同时在文档的位置 5 插入不同的字符,这里就可以通过创建 CRDT 的实例,然后将操作放入到 CRDT 实例里面来解决冲突。
const crdt = new CRDT(); // crdt.data = []
// 客户端A的插入操作
const operationA = { type: "insert", id: "A1", position: 5, content: "A" };
// 客户端B的插入操作
const operationB = { type: "insert", id: "B1", position: 5, content: "B" };
// 应用各自的操作
crdt.apply(operationA); // [ { id: 'A1', char: 'A' } ]
crdt.apply(operationB); // [ { id: 'A1', char: 'A' }, { id: 'B1', char: 'B' } ]
// 获取最终的数据
console.log(crdt.getData()); // AB
# 6. 离线编辑和数据同步
关键的要点:
- 本地存储编辑操作
- 重新联网的时候能够数据同步
- 冲突处理
1. 本地存储编辑操作
考虑使用 IndexedDB
// 打开或创建IndexedDB数据库
const request = indexedDB.open("offlineEditsDB", 1);
let db;
request.onupgradeneeded = (event) => {
db = event.target.result;
// 创建一个对象存储,用于存储编辑操作
const objectStore = db.createObjectStore("edits", { autoIncrement: true });
};
request.onsuccess = (event) => {
db = event.target.result;
};
request.onerror = (event) => {
console.error("IndexedDB error:", event.target.errorCode);
};
// 存储编辑操作到IndexedDB
function storeEditOperation(operation) {
const transaction = db.transaction(["edits"], "readwrite");
const objectStore = transaction.objectStore("edits");
objectStore.add(operation);
}
// 示例:存储插入操作
storeEditOperation({ type: 'insert', position: 5, content: 'A', timestamp: Date.now() });
2. 联网后数据同步
// 检查网络状态,监听 online 事件
window.addEventListener('online', syncOfflineEdits);
function syncOfflineEdits() {
// 首先从 Indexed 数据库里面获取离线编辑的内容
const transaction = db.transaction(["edits"], "readonly");
const objectStore = transaction.objectStore("edits");
const request = objectStore.getAll();
request.onsuccess = (event) => {
const operations = event.target.result;
if (operations.length > 0) {
// 同步操作到服务器
syncToServer(operations);
}
};
}
// 示例:同步操作到服务器
// 这里通过 HTTP 请求将离线编辑的内容发送到后端服务器
function syncToServer(operations) {
fetch('/sync-edits', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({ operations })
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
if (data.success) {
// 清空本地存储的操作
clearOfflineEdits();
}
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('Error syncing edits:', error);
});
}
// 清空本地存储的操作
function clearOfflineEdits() {
const transaction = db.transaction(["edits"], "readwrite");
const objectStore = transaction.objectStore("edits");
objectStore.clear();
}
3. 冲突处理
// 服务器端处理同步请求
app.post('/sync-edits', (req, res) => {
const operations = req.body.operations;
operations.forEach(operation => {
// 使用OT算法处理冲突,并应用操作
handleOperationWithOT(operation);
});
res.json({ success: true });
});
// 示例:使用OT算法处理操作
function handleOperationWithOT(operation) {
// 假设我们有一个全局的文档状态和操作列表
const transformedOperation = transformOperation(operation);
applyOperation(transformedOperation);
}
-EOF-